Kubernetes 執行器¶
注意
從 Airflow 2.7.0 版本開始,你需要安裝 cncf.kubernetes provider 包才能使用此執行器。可以透過安裝 apache-airflow-providers-cncf-kubernetes>=7.4.0 或透過安裝 Airflow 時包含 cncf.kubernetes 附加項來完成:pip install 'apache-airflow[cncf.kubernetes]'。
Kubernetes 執行器在 Kubernetes 叢集上為每個任務例項執行一個單獨的 pod。
KubernetesExecutor 作為 Airflow Scheduler 中的一個程序執行。排程器本身不一定需要在 Kubernetes 上執行,但需要訪問 Kubernetes 叢集。
KubernetesExecutor 需要後端使用非 sqlite 資料庫。
當 DAG 提交任務時,KubernetesExecutor 會向 Kubernetes API 請求一個 worker pod。然後 worker pod 執行任務,報告結果,並終止。
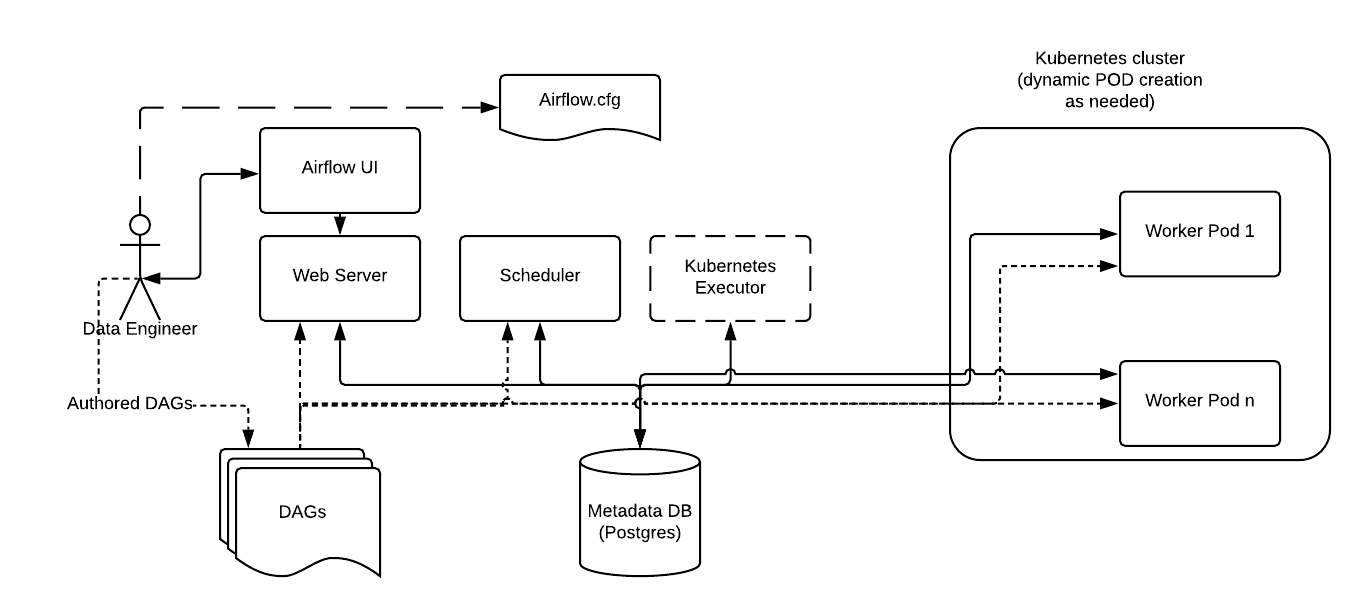
下面顯示了一個在 Kubernetes 叢集的五個分散式節點上執行的 Airflow 部署示例。
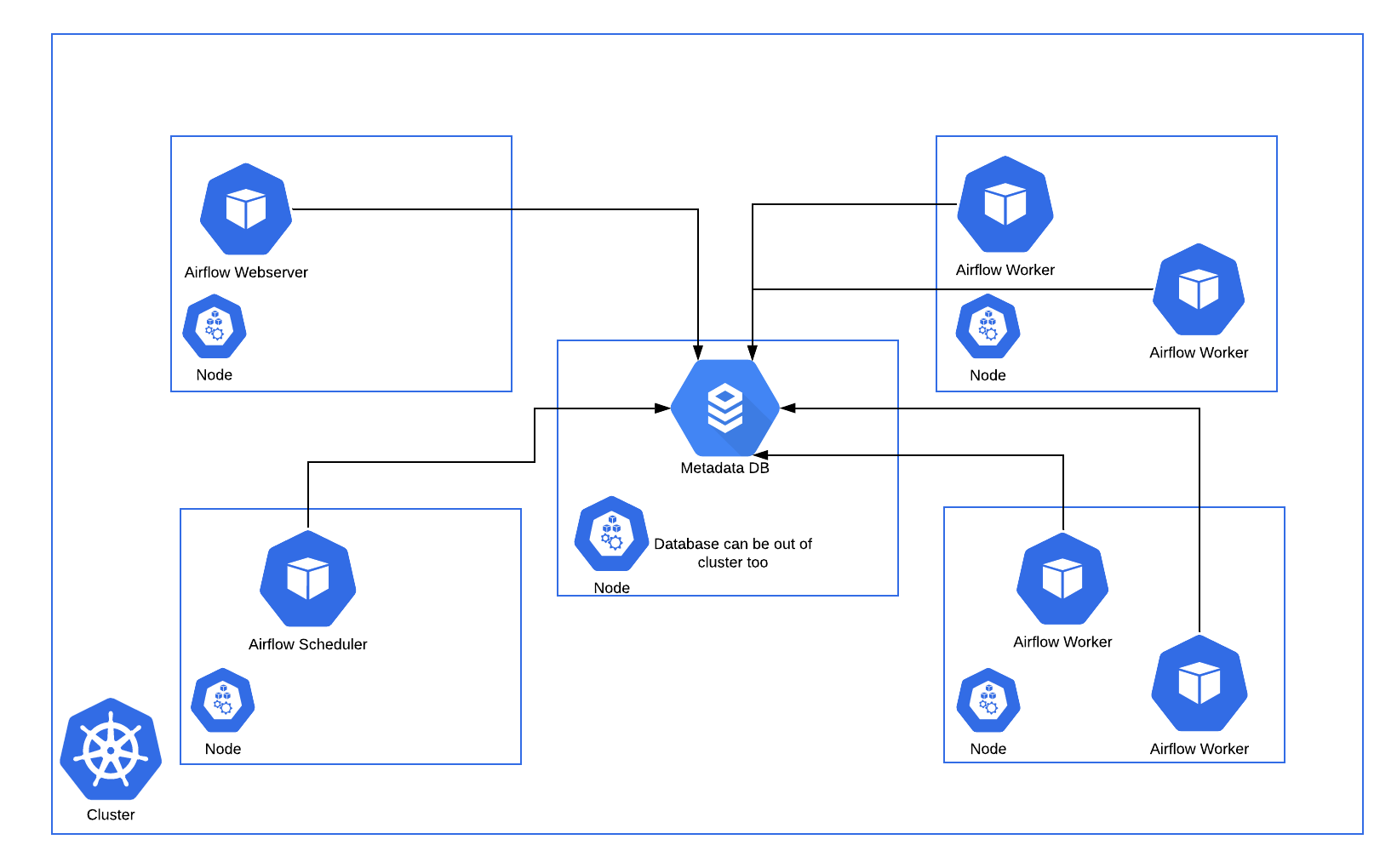
與常規 Airflow 架構一致,Worker 需要訪問 DAG 檔案以執行這些 DAG 中的任務並與元資料倉庫互動。此外,需要在 Airflow 配置檔案中指定 Kubernetes 執行器特有的配置資訊,例如 worker namespace 和映象資訊。
此外,Kubernetes 執行器還允許使用 Executor config 對每個任務指定附加功能。
配置¶
pod_template_file¶
為了自定義用於 k8s 執行器 worker 程序的 pod,你可以建立一個 pod 模板檔案。你必須在 airflow.cfg 的 kubernetes_executor 部分的 pod_template_file 選項中提供模板檔案的路徑。
Airflow 對 pod 模板檔案有兩個嚴格的要求:基礎映象和 pod 名稱。
基礎映象¶
pod_template_file 必須在 spec.containers[0] 位置有一個名為 base 的容器,並且必須指定其 image。
你可以在此必需容器之後自由建立 sidecar 容器,但 Airflow 假定 airflow worker 容器存在於容器陣列的開頭,並假定該容器名為 base。
注意
Airflow 可能會覆蓋基礎容器 image,例如透過 pod_override 配置;但它必須存在於模板檔案中且不能為空白。
Pod 名稱¶
必須在模板檔案中設定 pod 的 metadata.name。此欄位在啟動 pod 時總是會被動態設定,以保證所有 pod 的唯一性。但再次強調,它必須包含在模板中,且不能為空白。
示例 pod 模板¶
考慮到這些要求,以下是一些基本的 pod_template_file YAML 檔案示例。
注意
下面的示例在使用預設 Airflow 配置值時應該可以工作。但是,許多自定義配置值也需要透過此模板顯式地傳遞給 pod。這包括但不限於 sql 配置、必需的 Airflow 連線、DAGs 資料夾路徑和日誌設定。詳細資訊請參見 Configuration Reference。
將 DAGs 儲存在映象中
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: placeholder-name
spec:
containers:
- env:
- name: AIRFLOW__CORE__EXECUTOR
value: LocalExecutor
# Hard Coded Airflow Envs
- name: AIRFLOW__CORE__FERNET_KEY
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: RELEASE-NAME-fernet-key
key: fernet-key
- name: AIRFLOW__DATABASE__SQL_ALCHEMY_CONN
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: RELEASE-NAME-airflow-metadata
key: connection
- name: AIRFLOW_CONN_AIRFLOW_DB
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: RELEASE-NAME-airflow-metadata
key: connection
image: dummy_image
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: base
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: "/opt/airflow/logs"
name: airflow-logs
- mountPath: /opt/airflow/airflow.cfg
name: airflow-config
readOnly: true
subPath: airflow.cfg
restartPolicy: Never
securityContext:
runAsUser: 50000
fsGroup: 50000
serviceAccountName: "RELEASE-NAME-worker-serviceaccount"
volumes:
- emptyDir: {}
name: airflow-logs
- configMap:
name: RELEASE-NAME-airflow-config
name: airflow-config
將 DAGs 儲存在 persistentVolume 中
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: placeholder-name
spec:
containers:
- env:
- name: AIRFLOW__CORE__EXECUTOR
value: LocalExecutor
# Hard Coded Airflow Envs
- name: AIRFLOW__CORE__FERNET_KEY
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: RELEASE-NAME-fernet-key
key: fernet-key
- name: AIRFLOW__DATABASE__SQL_ALCHEMY_CONN
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: RELEASE-NAME-airflow-metadata
key: connection
- name: AIRFLOW_CONN_AIRFLOW_DB
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: RELEASE-NAME-airflow-metadata
key: connection
image: dummy_image
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: base
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: "/opt/airflow/logs"
name: airflow-logs
- mountPath: /opt/airflow/dags
name: airflow-dags
readOnly: true
- mountPath: /opt/airflow/airflow.cfg
name: airflow-config
readOnly: true
subPath: airflow.cfg
restartPolicy: Never
securityContext:
runAsUser: 50000
fsGroup: 50000
serviceAccountName: "RELEASE-NAME-worker-serviceaccount"
volumes:
- name: airflow-dags
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: RELEASE-NAME-dags
- emptyDir: {}
name: airflow-logs
- configMap:
name: RELEASE-NAME-airflow-config
name: airflow-config
從 git 拉取 DAGs
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: dummy-name
spec:
initContainers:
- name: git-sync
image: "registry.k8s.io/git-sync/git-sync:v3.6.3"
env:
- name: GIT_SYNC_BRANCH
value: "v2-2-stable"
- name: GIT_SYNC_REPO
value: "https://github.com/apache/airflow.git"
- name: GIT_SYNC_DEPTH
value: "1"
- name: GIT_SYNC_ROOT
value: "/git"
- name: GIT_SYNC_DEST
value: "repo"
- name: GIT_SYNC_ADD_USER
value: "true"
- name: GIT_SYNC_ONE_TIME
value: "true"
volumeMounts:
- name: airflow-dags
mountPath: /git
containers:
- env:
- name: AIRFLOW__CORE__EXECUTOR
value: LocalExecutor
# Hard Coded Airflow Envs
- name: AIRFLOW__CORE__FERNET_KEY
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: RELEASE-NAME-fernet-key
key: fernet-key
- name: AIRFLOW__DATABASE__SQL_ALCHEMY_CONN
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: RELEASE-NAME-airflow-metadata
key: connection
- name: AIRFLOW_CONN_AIRFLOW_DB
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: RELEASE-NAME-airflow-metadata
key: connection
image: dummy_image
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: base
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: "/opt/airflow/logs"
name: airflow-logs
- mountPath: /opt/airflow/dags
name: airflow-dags
subPath: repo/airflow/example_dags
readOnly: false
- mountPath: /opt/airflow/airflow.cfg
name: airflow-config
readOnly: true
subPath: airflow.cfg
restartPolicy: Never
securityContext:
runAsUser: 50000
fsGroup: 50000
serviceAccountName: "RELEASE-NAME-worker-serviceaccount"
volumes:
- name: airflow-dags
emptyDir: {}
- name: airflow-logs
emptyDir: {}
- configMap:
name: RELEASE-NAME-airflow-config
name: airflow-config
pod_override¶
使用 KubernetesExecutor 時,Airflow 提供了按任務覆蓋系統預設設定的功能。要利用此功能,請建立一個 Kubernetes V1pod 物件並填寫所需的覆蓋設定。
要覆蓋由 KubernetesExecutor 啟動的 pod 的基礎容器,建立一個包含單個容器的 V1pod,並按如下方式覆蓋欄位
airflow/example_dags/example_kubernetes_executor.py
executor_config_volume_mount = {
"pod_override": k8s.V1Pod(
spec=k8s.V1PodSpec(
containers=[
k8s.V1Container(
name="base",
volume_mounts=[
k8s.V1VolumeMount(mount_path="/foo/", name="example-kubernetes-test-volume")
],
)
],
volumes=[
k8s.V1Volume(
name="example-kubernetes-test-volume",
host_path=k8s.V1HostPathVolumeSource(path="/tmp/"),
)
],
)
),
}
@task(executor_config=executor_config_volume_mount)
def test_volume_mount():
"""
Tests whether the volume has been mounted.
"""
with open("/foo/volume_mount_test.txt", "w") as foo:
foo.write("Hello")
return_code = os.system("cat /foo/volume_mount_test.txt")
if return_code != 0:
raise ValueError(f"Error when checking volume mount. Return code {return_code}")
volume_task = test_volume_mount()
請注意,以下欄位都將被擴充套件而不是覆蓋。來自 spec:volumes 和 init_containers。來自 container:volume mounts、environment variables、ports 和 devices。
要向啟動的 pod 新增 sidecar 容器,建立一個包含空的第一容器(名稱為 base)和第二個包含所需 sidecar 的容器的 V1pod。
airflow/example_dags/example_kubernetes_executor.py
executor_config_sidecar = {
"pod_override": k8s.V1Pod(
spec=k8s.V1PodSpec(
containers=[
k8s.V1Container(
name="base",
volume_mounts=[k8s.V1VolumeMount(mount_path="/shared/", name="shared-empty-dir")],
),
k8s.V1Container(
name="sidecar",
image="ubuntu",
args=['echo "retrieved from mount" > /shared/test.txt'],
command=["bash", "-cx"],
volume_mounts=[k8s.V1VolumeMount(mount_path="/shared/", name="shared-empty-dir")],
),
],
volumes=[
k8s.V1Volume(name="shared-empty-dir", empty_dir=k8s.V1EmptyDirVolumeSource()),
],
)
),
}
@task(executor_config=executor_config_sidecar)
def test_sharedvolume_mount():
"""
Tests whether the volume has been mounted.
"""
for i in range(5):
try:
return_code = os.system("cat /shared/test.txt")
if return_code != 0:
raise ValueError(f"Error when checking volume mount. Return code {return_code}")
except ValueError as e:
if i > 4:
raise e
sidecar_task = test_sharedvolume_mount()
你還可以按任務建立自定義 pod_template_file,以便在多個任務之間重用相同的基礎值。這將替換 airflow.cfg 中命名的預設 pod_template_file,然後使用 pod_override 覆蓋該模板。該 pod_template_file 也將用於生成在 Airflow UI 中可見的 Pod K8s Spec。
以下是一個具有這兩個功能的任務示例
import os
import pendulum
from airflow import DAG
from airflow.decorators import task
from airflow.example_dags.libs.helper import print_stuff
from airflow.settings import AIRFLOW_HOME
from kubernetes.client import models as k8s
with DAG(
dag_id="example_pod_template_file",
schedule=None,
start_date=pendulum.datetime(2021, 1, 1, tz="UTC"),
catchup=False,
tags=["example3"],
) as dag:
executor_config_template = {
"pod_template_file": os.path.join(AIRFLOW_HOME, "pod_templates/basic_template.yaml"),
"pod_override": k8s.V1Pod(metadata=k8s.V1ObjectMeta(labels={"release": "stable"})),
}
@task(executor_config=executor_config_template)
def task_with_template():
print_stuff()
管理 DAGs 和日誌¶
使用持久卷是可選的,取決於你的配置。
Dags:
要將 DAGs 放入 worker 中,你可以
在映象中包含 DAGs。
使用
git-sync,它會在啟動 worker 容器之前執行一個git pull來拉取 DAGs 倉庫。將 DAGs 儲存在持久捲上,該持久卷可以掛載到所有 worker 上。
日誌:
要從 worker 中獲取任務日誌,你可以
使用同時掛載到 webserver 和 worker 上的持久卷。
啟用遠端日誌記錄。
注意
如果你未啟用日誌持久化,並且未啟用遠端日誌記錄,則 worker pod 關閉後日志將丟失。
與 CeleryExecutor 的比較¶
與 CeleryExecutor 不同,KubernetesExecutor 不需要額外的元件(如 Redis),但需要訪問 Kubernetes 叢集。
此外,可以使用 Kubernetes 內建的監控功能來監控 Pod。
使用 KubernetesExecutor,每個任務都在其自己的 pod 中執行。pod 在任務排隊時建立,並在任務完成時終止。從歷史上看,在諸如可突發工作負載之類的場景中,這比 CeleryExecutor 具有資源利用優勢,因為 CeleryExecutor 需要固定數量的長時間執行的 Celery worker pod,無論是否有任務執行。
然而,官方的 Apache Airflow Helm chart 可以根據佇列中的任務數量將 celery worker 自動縮減到零,因此在使用官方 chart 時,這不再是一個優勢。
使用 Celery worker,你的任務延遲往往會更低,因為在任務排隊時 worker pod 已經啟動並執行。另一方面,由於多個任務在同一個 pod 中執行,使用 Celery 時你可能需要更注意任務設計中的資源利用,特別是記憶體消耗。
KubernetesExecutor 有用的一種場景是當你有長時間執行的任務時,因為如果在任務執行時進行部署,任務將一直執行直到完成(或超時等)。但使用 CeleryExecutor,如果你設定了寬限期,任務只會執行到寬限期結束,屆時任務將被終止。KubernetesExecutor 適用於的另一種場景是當你的任務在資源需求或映象方面不是很統一時。
最後,請注意這並非二選一;使用 CeleryKubernetesExecutor,可以在同一個叢集上同時使用 CeleryExecutor 和 KubernetesExecutor。CeleryKubernetesExecutor 將檢視任務的 queue 來決定是在 Celery 還是 Kubernetes 上執行。預設情況下,任務會發送到 Celery worker,但如果你想使用 KubernetesExecutor 執行任務,則將其傳送到 kubernetes queue,它將在其自己的 pod 中執行。無論你使用哪種執行器,KubernetesPodOperator 都可以達到類似的效果。
容錯¶
提示
要排除 KubernetesExecutor 的問題,你可以使用 airflow kubernetes generate-dag-yaml 命令。此命令會生成在 Kubernetes 中將要啟動的 pod,並將其輸出到 yaml 檔案供你檢查。
處理 Worker Pod 崩潰¶
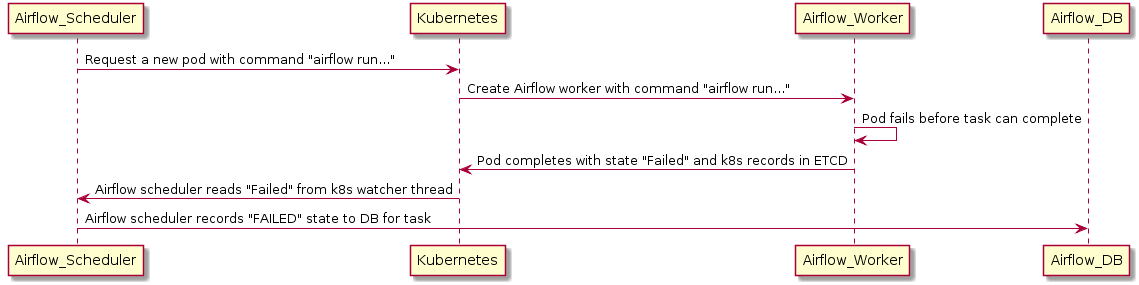
在處理分散式系統時,我們需要一個假定任何元件在任何時候都可能因 OOM 錯誤到節點升級等原因而崩潰的系統。
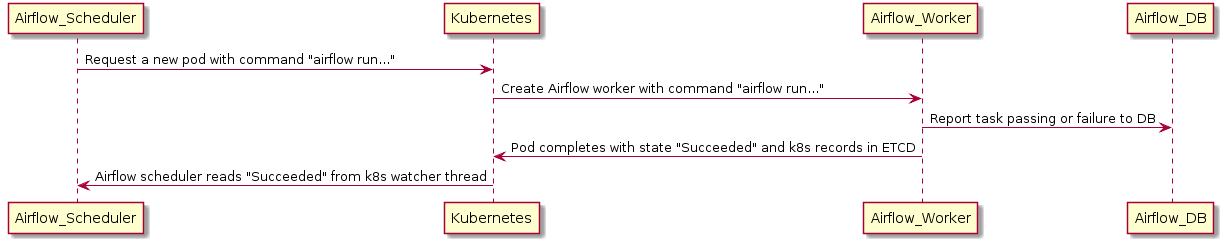
如果 worker 在向後端 DB 報告其狀態之前死亡,執行器可以使用 Kubernetes watcher 執行緒來發現失敗的 pod。
Kubernetes watcher 是一個執行緒,可以訂閱 Kubernetes 資料庫中發生的每一個變化。當 pod 啟動、執行、結束和失敗時,它會收到警報。透過監控此流,KubernetesExecutor 可以發現 worker 已崩潰,並正確地將任務報告為失敗。
但是排程器 Pod 崩潰怎麼辦?¶
在排程器崩潰的情況下,排程器將使用 watcher 的 resourceVersion 恢復其狀態。
當監控 Kubernetes 叢集的 watcher 執行緒時,每個事件都有一個單調遞增的數字,稱為 resourceVersion。執行器每次讀取 resourceVersion 時,都會將最新值儲存在後端資料庫中。由於儲存了 resourceVersion,排程器可以重新啟動並從上次中斷的地方繼續讀取 watcher 流。由於任務獨立於執行器執行並直接向資料庫報告結果,排程器故障不會導致任務失敗或重新執行。